
SEFARI provides the research needed to improve the efficiency and resilience of Scotland’s food production systems whilst protecting the environment and our rural communities. SEFARI works on improving our crop production systems, and reducing the impacts of plant disease. For livestock, work on animal characteristics and health and welfare leads to more efficient livestock production, which in turn reduces waste, lowers greenhouse gas emissions and improves global food security.
Sector Contact

Case Studies

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing concern not only in hospitals but also in our farms and fields. When pathogenic bacteria acquire AMR, antimicrobials previously used to treat them are no longer effective causing a greater burden of disease. The use of antimicrobials in livestock can lead to increasing emergence of AMR which can spread more widely in the environment when farmyard manure or slurry is used as organic fertiliser to improve soil health and productivity in grasslands.
This blog delves into a five-year project (we’re at the halfway point!), aimed at exploring how different fertilisation practices, including biosolids from sewage sludge, influence the dynamics of AMR in pasture ecosystems. The research investigates whether sewage sludge pellets (biosolids) might offer a safer alternative to traditional animal-derived fertilisers.
Farm animals near a human dwelling (Credit: Nuno Silva)
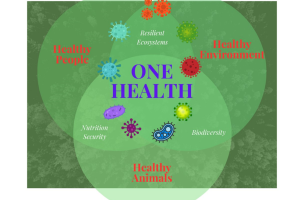
Antimicrobial resistance is an emerging threat to the health of animals and humans in Scotland and around the world. SEFARI scientists at the Rowett Institute have made some early, exciting findings that may prove invaluable in the global battle to hold back the spread of anti-microbial resistance. This blog post discusses the ongoing Scottish Government’s RESAS funded studies that are identifying environmental bacterial isolates that are showing promise for development as probiotics to inhibit antibiotic resistant bacteria across different ecosystems.
Illustration: Microbial ecosystems and One Health (Credit: authors)

Climate Change Adaptation is one of the key items on the policy agenda in Scotland, and this was the main focus at this year’s ENRA Science, Evidence and Policy conference.
Organised by the Scottish Government’s Rural & Environmental Science and Analytical Services (RESAS) and held at Edinburgh’s Dynamic Earth, the conference brought together researchers and policymakers from across the rural and environment research and policy landscape in Scotland and showcased Scottish Government (RESAS) funded research evidence that is supporting climate change adaptation.
Title Image: Opening keynote by Prof Mathew Williams (Photo by Alöna Roitershtein)

Climate-positive farming is key to Scotland’s climate change adaptation and mitigation.
In this blog, Prof Lorna Dawson, Knowledge Broker for Environment, reflects on her visit to the Climate-Positive Farming Initiative at the James Hutton Institute's Glensaugh Farm.

Reproductive diseases in sheep and cattle pose significant economic challenges. Therefore, SEFARI researchers at the Moredun Research Institute, funded by the Scottish Government’s Strategic Research Programme, are pioneering the development of new vaccines to tackle these issues. In particular, our focus is on preventing abortions and stillbirths in sheep caused by Chlamydia abortus (enzootic abortion of ewes also known as ovine enzootic abortion or ovine chlamydiosis) and in cattle due to Neospora caninum (neosporosis). In this blog, we delve into the importance of these diseases for livestock producers, the need for innovative reproductive vaccines, and the strategies being employed to develop these vaccines.
Sheep on grass. (Source: Moredun communications archive)

SEFARI Gateway are a silver sponsor at this year’s A3 Scotland conference - a not-for-profit two-day conference for the Animal Health, Agritech and Aquaculture (AAA) sectors, attracting attendees from all over the world to Inverness, to participate in plenaries, breakouts, investor panel and start up pitching, and sessions on funding, international showcase, skills and emerging solutions in AI, robotics, and sensors.
Our work across the Scottish Government’s Environment, Natural Resources and Agriculture (ENRA) Strategic Research Portfolio makes a substantial contribution to the A3 sector in Scotland. Read on to find out more about our A3 related work.
Cattle in Orkney (Photo by Alöna Roitershtein)

A significant challenge for sheep farmers has always been gut worm infections that damage the digestive systems of lambs, resulting in poor growth and reduced economic and environmental sustainability. The worms have developed resistance to the anthelmintic drugs used to control them, necessitating alternative control strategies. One such strategy is grazing management. Therefore, SEFARI Researchers are investigating if what, and how, sheep graze could influence worm control strategies.
Sheep grazing in one of the set-stocked paddocks (Credit: Andrew Kelloe)

Ticks and tick-borne diseases (TBDs) are of growing concern in Scotland and the UK due to factors like climate change, wildlife distribution shifts, and changes in land use. This has led to increased tick burden in livestock and Tick-borne diseases (TBDs) outbreaks appearing in new areas, posing threats to livestock and public health.
Current control methods like acaricides (pesticides to kill ticks and mites) face challenges, such as treatment failures and environmental harm. Effective control requires a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders, fostering comprehension of conflicting matters and leading to the formation of a new cross-sectoral network. In response to this pressing issue, we have organised a SEFARI Gateway funded Innovative Knowledge Exchange workshop to identify best practice and produce industry guidelines for ticks and TBDs control.
Title image: Sheep in long grass (Credit: Moredun Research Institute)

During this year’s GO Falkland gathering, in the foothills of the mighty East Lomond Hill on the beautiful Falkland estate, an enthusiastic collective of farmers, growers, artists, scientists and policymakers came together to discuss what Regenerative Farming, Forestry, Land Use and Food means for them. During the event, we shared experiences and insight to collaboratively work towards the shared goals of the sustainable future.
SEFARI and SEFARI Gateway were there to contribute to and support these conversations over the two days. Find out more in this blog.

Fineview, a dairy farm managed by the Clark family in Dumfries and Galloway, is part of the innovative First Milk dairy cooperative which aims to deliver healthy fresh milk on sound environmental principles. Why not take a virtual tour and hear how delivering quality milk products needs a nurtured healthy soil, the encouragement of biodiversity, healthy cows and a sustainable farm enterprise.
This virtual tour is one of a series of SEFARI Gateway Innovative Knowledge Exchange funded tours designed to provide you with access to the many research facilities across Scotland whilst also giving you a taste of some of the work we do. Across SEFARI, world leading pioneering research is being undertaken that can really make a difference on the ground.

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the biggest health-threats of modern time. A global survey in 2019 showed that it claimed more lives than HIV/AIDS or malaria, and AMR is one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity. Resistance to current drugs continues to emerge and grow, and there are insufficient new interventions on the horizon. This has left us in a precarious position, for which the World Health Organisation has developed a global strategy to help address the problem.
In this blog we explain how we have mapped out the research activities in Scotland related to AMR, providing a useful and needed overview of the type of ongoing AMR work and who is involved, and how, through SEFARI Gateway funding, we can develop this into an online resource.

Here at SEFARI, we take pride in our partner institutes and their outstanding achievements in research and informing policy. We firmly believe that inequality in the sustainability sector must be addressed and are committed to using our platforms to showcase and commend remarkable women at all stages of their careers. Read on to celebrate the accomplishments of some of the outstanding SEFARI women.
The Moredun Research Institute (one of SEFARI’s members) alongside the Universities of Dundee, Edinburgh and Glasgow are forming a new and exciting network, called Scottish Parasitology Partnership in Research, Innovation, and Training (SPPIRIT), to support Scotland’s eminent parasitology research.
In this blog, Moredun Fellow, Dr David Smith highlights Scotland’s long contribution to parasitology, the platform this new network could offer to early career researchers and how you can ‘join in’ the SPPIRIT.

The climate emergency affects every part of our lives and collaboration within and across sectors is therefore key to addressing this crisis. With collaboration at their core, Scotland’s five Centres of Expertise (CoE) work together to connect research with, and respond to, policy needs across issues which affect the climate, water, animal and plant health, land and communities.
In this blog, you can learn more about the work of the CoEs - namely Centre of Expertise for Waters (CREW), ClimateXChange (CXC), Epidemiology, Population health and Infectious disease Control (EPIC), Plant Health Centre (PHC) and SEFARI Gateway - and how during COP26 they came together to host a series of events at the University of Glasgow to showcase how they are helping to protect people and the environment from the effects of climate change.

Even though COP26 is now over, there is still a strong focus on initiatives being taken by countries to address climate change. Scotland is committed to reaching net zero by 2045 and to delivering leadership and collaboration within the global response to tackling climate change.
In this blog, Lorna highlights her work in the creation of new resources which outline what is going on across the Centres of Expertise (CoE) to inform and support policy for climate action. Collation of this material from across the Centres was funded by SEFARI Gateway.

COP26, the United Nations Climate Change conference held in Glasgow, ended on Saturday the 13th of November. Since then, there has been a lot of stock taking as to what was achieved under the Glasgow Climate Pact. Several gains emerged in the first week of the conference, with the announcement of collective action on deforestation, coal, finance and methane. It is the latter of these, the Global Methane Pledge (GMP), which could provide immediate gains to limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees, as embedded in the Paris Agreement. In this blog article, we explain why cutting methane emissions is an imperative and provide examples of how Scottish Government funded science is helping farmers and food consumers reduce their emissions.

With the UN Climate Change Conference (COP26) underway, there is a spotlight on initiatives being taken by countries to address climate change. Do you want to know what Scotland is doing about it? Then join us on a virtual tour of some of SEFARI’s fascinating climate research.
From exploring windy Aberdeen Bay to visiting Scotland’s marshy peatlands, the tours offer a behind the scenes look at some of our innovative research which is seeking to help Scotland address and adapt to the climate crises. What’s more, you can enjoy the experience from the comfort of your own sofa and at your own pace.

In September, colleagues from the Moredun Research Institute, SEFARI Gateway, the Food and Drink Federation Scotland (FDF Scotland), Royal Highland Educational Trust (RHET) and Quality Meat Scotland (QMS) outlined a wealth of educational resources that cover the sustainability of key resources such as food, water, and energy. A key priority for the younger generation especially with COP26 on the horizon, and on our doorstep!
By joining forces at a continuing professional development (CPD) event, organised by the Scottish Schools Education Resources Centre (SSERC), our session was designed to support teachers with the delivery of National 4, 5 and Higher Environmental Science. The session ended by moving outside of the classroom to see the new mobile laboratory and education bus, created as part of Moredun’s centenary, which is being used to visit schools and engage children with different science topics. Seeing the bus gave us the opportunity to extend discussions in a more relaxed environment out in the autumn sunshine.

Zoonotic pathogens are microorganisms transmitted by animals, which cause disease and illness in humans. Many of them are foodborne and are commonly associated with farmed animals, or less frequently with wildlife. However, some pathogens are also transmitted into the food-chain indirectly from animals onto plants, via faecal contamination of water used for irrigation or via the soil where the plants grow. If the plants are destined for consumption, e.g., fruit and vegetable crops that are normally consumed raw or minimally processed, this can become a foodborne hazard.
Surprisingly though, there is still a misconception that plants play only a minor role in zoonoses survival and spread, even though fresh-produce accounts for similar numbers of foodborne outbreaks as meat or dairy. At SEFARI our researchers contribute to work in this area and are part of only a relatively small number of researchers in the UK & Ireland who do. In this blog, Dr Nicola Holden discusses how SEFARI research fits into this complex issue, outlines the key risk factors (illustrated with examples) and identifies what questions still need to be addressed.

With the pandemic turning our lives upside down, the use of digital communication has accelerated overnight. Webinars, Teams meetings, Digital classrooms, Virtual brainstorming boards, to name but a few. They have all helped in keeping us connected from the safety of our own homes. However, these virtual technologies achieve so much more than simply enabling conversations to continue. They have removed barriers - social, physical, economic, geographical - and in removing these barriers they have made research more accessible.
In this blog, Dr Lorna Cole, discusses the recent creation of a series of virtual tours at five of our leading SEFARI research farms, in a SEFARI Gateway Responsive Opportunity funded project. The tours are readily accessible through the Google Earth platform, giving everyone access to the countryside and allowing us to learn more about the research that is being conducted on SEFARI’s research farms.
Pagination
Blog

Digging into the Problem: AMR in Agricultural Ecosystems
The use of antimicrobials in livestock farming has proven essential for maintaining animal health, but are known to contain resistant bacteria due to the use of antimicrobials in livestock.

Following the success of the first ENRA Science, Evidence and Policy conference last year, the conference returned this year to provide a forum to discuss key cross cutting strategic issues affecting Scotland’s environment