
Scotland’s agriculture sector underpins Scotland’s high performing food and drink industry, is at the heart of our rural communities, and provides benefits to wider society. SEFARI provides the research needed for Scotland to improve the efficiency of good food production whilst protecting the environment, rural communities and animal welfare. This is done through developing tools (for example on disease control, welfare and genetics), research, and the capability to think about agriculture in a wider context. We also work with farmers and growers, processors, food companies, health professionals, nutritionists, and economists to find ways to put our research into practice.
Sector Contact

Case Studies

In this blog Professor Lorna Dawson, Gateway knowledge broker for Environment and Soil, shares some insights after visiting RBGE in August 2025. SEFARI Gateway worked with Scotia Agricultural Club to orchestrate this interesting and inspiring visit to the garden. Scotia Agriculture Group has the aim of bringing together people with experience of interdisciplinary approaches to food production and seek a balanced judgement of the long term effects of innovation on the conservation of the land. Certainly there was a lot of innovative and interesting work going on at RBGE to inspire the group.
SEFARI Gateway provides bespoke access to the RESAS portfolio’s research expertise and analysis to ensure scientific evidence helps inform the health, wealth and well-being of Scotland’s people. The Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE) is part of the SEFARI collective (i.e. Moredun, James Hutton Institute, SRUC, Rowett, BioSS, RBGE) supporting the current and next generation of researchers to ensure the science undertaken has real world impact.

SRUC, Craibstone and Tulloch, 8 July 2025
In this blog Professor Lorna Dawson, Gateway knowledge broker for Environment and Soil, shares some insights after attending a meeting on the field trial information underpinning sustainable food and feed production through a sound scientific understanding. The meeting encompassed a series of brilliant talks outlining the science behind the stories, followed by a tour of several field experiments in the Aberdeenshire area.

Infectious diseases of farmed animals are important threats to agriculture in Scotland, causing significant animal suffering, and economic losses to farmers. Typically, these infections are treated with antibiotics, but the rise of antibiotic-resistant germs means additional strategies are needed to reduce diseases on farms. This blog describes ongoing work at The Rowett Institute to harness the beneficial collection of microbes (“microbiota”) that lives within livestock animals as novel approaches to protect against infectious diseases.
Scientists at The James Hutton Institute are spearheading cutting-edge research to support the UK’s National Action Plan for pesticide reduction, combining AI, big data, and biology to revolutionise Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in Scotland. From forecasting potato virus risks to advancing biological alternatives to conventional pesticides, their work helps farmers target pesticide use while safeguarding yields and the environment. Underpinned by RESAS funding, this science-driven approach is reshaping pest management, ensuring sustainable farming and future-proofing Scotland’s vital agricultural sector.

The British Society of Animal Science is a charitable organization, which has been in existence for over 80 years! It is also the principal learned body supporting animal science in the UK. BSAS works ‘to advance the sector, improve the understanding of all aspects of animal science and ensure research and knowledge transfer has a practical and beneficial application’. Its annual scientific conference regularly attracts delegates from across the world, this year was no exception, with approximately 400 delegates from 23 countries. The conference was held in sunny Galway on the stunning Wild Atlantic Way in the west of Ireland, from 8th-10th April.

Finding innovative ways to engage a wider audience is an ongoing challenge for researchers. Here at SEFARI, we are no less prone to these challenges and strive to ensure that our work generates valuable insights and reaches everyone in engaging ways. In this blog, read about one of our latest Innovative Knowledge Exchange (IKE) funded projects, the CROPsim Project, a tool that uses gaming technology to bridge the gap between cutting-edge agriculture research and those interested in sustainable farming practices.
CROPSim in action (Credit: project team)

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing concern not only in hospitals but also in our farms and fields. When pathogenic bacteria acquire AMR, antimicrobials previously used to treat them are no longer effective causing a greater burden of disease. The use of antimicrobials in livestock can lead to increasing emergence of AMR which can spread more widely in the environment when farmyard manure or slurry is used as organic fertiliser to improve soil health and productivity in grasslands.
This blog delves into a five-year project (we’re at the halfway point!), aimed at exploring how different fertilisation practices, including biosolids from sewage sludge, influence the dynamics of AMR in pasture ecosystems. The research investigates whether sewage sludge pellets (biosolids) might offer a safer alternative to traditional animal-derived fertilisers.
Farm animals near a human dwelling (Credit: Nuno Silva)

The interaction between nutrient management, food production and sustainability goals are complex, where both research and policy still remain fragmented. The report from the Nutrient Management Expert Group (NMEG), commissioned by DEFRA to tackle this complexity, was published in May 2024, containing the detailed assessment of the key policy and 15 recommendations. This blog summarises the key takeaways from this work.
Slurry Spreader (Credit: Saxifraga, Harry van Oosterhout, CC BY-NC-SA)
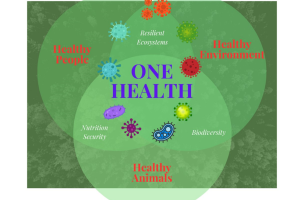
Antimicrobial resistance is an emerging threat to the health of animals and humans in Scotland and around the world. SEFARI scientists at the Rowett Institute have made some early, exciting findings that may prove invaluable in the global battle to hold back the spread of anti-microbial resistance. This blog post discusses the ongoing Scottish Government’s RESAS funded studies that are identifying environmental bacterial isolates that are showing promise for development as probiotics to inhibit antibiotic resistant bacteria across different ecosystems.
Illustration: Microbial ecosystems and One Health (Credit: authors)

To mark this year’s International Day of Rural Women, our colleague Ana Vuin from Rural Policy Centre at SRUC, offers her insight on the role of women in agriculture and rural communities, challenges of representation, health and wellbeing, as well as opportunities to foster inclusive and fair rural society.
Title image: Hands together (Photo by Hannah Busing, Unsplash)

Climate Change Adaptation is one of the key items on the policy agenda in Scotland, and this was the main focus at this year’s ENRA Science, Evidence and Policy conference.
Organised by the Scottish Government’s Rural & Environmental Science and Analytical Services (RESAS) and held at Edinburgh’s Dynamic Earth, the conference brought together researchers and policymakers from across the rural and environment research and policy landscape in Scotland and showcased Scottish Government (RESAS) funded research evidence that is supporting climate change adaptation.
Title Image: Opening keynote by Prof Mathew Williams (Photo by Alöna Roitershtein)

Climate-positive farming is key to Scotland’s climate change adaptation and mitigation.
In this blog, Prof Lorna Dawson, Knowledge Broker for Environment, reflects on her visit to the Climate-Positive Farming Initiative at the James Hutton Institute's Glensaugh Farm.

Reproductive diseases in sheep and cattle pose significant economic challenges. Therefore, SEFARI researchers at the Moredun Research Institute, funded by the Scottish Government’s Strategic Research Programme, are pioneering the development of new vaccines to tackle these issues. In particular, our focus is on preventing abortions and stillbirths in sheep caused by Chlamydia abortus (enzootic abortion of ewes also known as ovine enzootic abortion or ovine chlamydiosis) and in cattle due to Neospora caninum (neosporosis). In this blog, we delve into the importance of these diseases for livestock producers, the need for innovative reproductive vaccines, and the strategies being employed to develop these vaccines.
Sheep on grass. (Source: Moredun communications archive)

SEFARI Gateway are a silver sponsor at this year’s A3 Scotland conference - a not-for-profit two-day conference for the Animal Health, Agritech and Aquaculture (AAA) sectors, attracting attendees from all over the world to Inverness, to participate in plenaries, breakouts, investor panel and start up pitching, and sessions on funding, international showcase, skills and emerging solutions in AI, robotics, and sensors.
Our work across the Scottish Government’s Environment, Natural Resources and Agriculture (ENRA) Strategic Research Portfolio makes a substantial contribution to the A3 sector in Scotland. Read on to find out more about our A3 related work.
Cattle in Orkney (Photo by Alöna Roitershtein)

A significant challenge for sheep farmers has always been gut worm infections that damage the digestive systems of lambs, resulting in poor growth and reduced economic and environmental sustainability. The worms have developed resistance to the anthelmintic drugs used to control them, necessitating alternative control strategies. One such strategy is grazing management. Therefore, SEFARI Researchers are investigating if what, and how, sheep graze could influence worm control strategies.
Sheep grazing in one of the set-stocked paddocks (Credit: Andrew Kelloe)

Ticks and tick-borne diseases (TBDs) are of growing concern in Scotland and the UK due to factors like climate change, wildlife distribution shifts, and changes in land use. This has led to increased tick burden in livestock and Tick-borne diseases (TBDs) outbreaks appearing in new areas, posing threats to livestock and public health.
Current control methods like acaricides (pesticides to kill ticks and mites) face challenges, such as treatment failures and environmental harm. Effective control requires a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders, fostering comprehension of conflicting matters and leading to the formation of a new cross-sectoral network. In response to this pressing issue, we have organised a SEFARI Gateway funded Innovative Knowledge Exchange workshop to identify best practice and produce industry guidelines for ticks and TBDs control.
Title image: Sheep in long grass (Credit: Moredun Research Institute)

Supported by SEFARI GAteway, the Royal Bank of Scotland, the RSA, and in particular the RSA Fellows Borders Network and the RSA Fellows Rural and Environmental Issues network Scotland and NFU Mutual, over 100 guests attended the Business breakfast from 8:30 until 10:30, in the Members Marquee, organised and welcomed by RSA fellow Mrs Ann Packard, FRSA, HonFRIAS.

During this year’s GO Falkland gathering, in the foothills of the mighty East Lomond Hill on the beautiful Falkland estate, an enthusiastic collective of farmers, growers, artists, scientists and policymakers came together to discuss what Regenerative Farming, Forestry, Land Use and Food means for them. During the event, we shared experiences and insight to collaboratively work towards the shared goals of the sustainable future.
SEFARI and SEFARI Gateway were there to contribute to and support these conversations over the two days. Find out more in this blog.

What do hemp, barley, antimicrobial resistance and soft fruits have in common? They are the episode themes for a series of podcasts that SEFARI and SEFARI Gateway has created in partnership with OnFARM. So, if you’re a farmer, grower, food producer or simply interested in the science behind what we eat and where it comes from, then this is the 4-part series for you. Enjoy!

After a winter of unceasing heavy rains, and many farmers struggling to get into the field for spring sowing or to re-sow damaged autumn crops, it’s been a difficult start to the 2024 growing season. Agriculture is already having to cope with climatic shifts, while at the same time trying to reduce its environmental impact, reduce its contributions to further climate change, and still turn a profit.
What does this mean for the arable sector – how is it adapting? And what will increase farm resilience to these conditions? These are the questions that will be tackled in this year’s Arable Scotland event, on Tuesday 2nd July at the James Hutton Institute’s Balruddery Farm, near Dundee. Now in its sixth year, this free event brings together key stakeholders in arable production to delve into crucial industry topics and highlight innovative practices for sustainable and resilient farming.
Pagination
Blog


Importance of farmed animals to Scotland